Staphylococcus infection is a major health concern as a lot of people are living with it. The symptoms depend on where the carrier is infected, and even though most aren’t serious, it can be life-threatening.
What You Should Know About Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (Mrsa)?
Staphylococcus aureus (SA) is a bacterium that is present on the skin or in the nose of about three out of ten healthy persons. A lot of people are not aware that they are carrying the bacteria.
When the SA bacteria are in present your nose or on your skin, they usually do not cause any harm. However, if these bacteria find their way into or through your skin, you will experience a variety of infections, such as wound and skin infections. Occasionally, these bacteria can lead to serious infections in your lungs, blood, or other tissues.
MRSA bacteria are forms of the Staph bacteria that have developed a resistance to several antibiotics that are usually used to treat Staphylococcus infections. MRSA was once discovered in hospitals, but now, new strains of MRSA associated with the community are now approximately 1 out of 5 in community Staphylococcus infections.
MRSA has raised a lot of like if it lives on surfaces and other objects and how long it can live before it dies. This guide will answer all major questions related to MRSA and how long it lives on furniture and other surfaces.
How long does MRSA live on furniture?
(MRSA) can live on certain surfaces, like furniture, towels, razors, as well as athletic equipment for hours, days, and even weeks. These bacteria can spread to people who come in contact with a contaminated surface. These bacteria can result in an infectionan infection if it finds its way into a scrape, cut, or an open wound.
Can You Get MRSA From Your Furniture?
According to a new study, people whose household furniture and other appliances and objects are contaminated with MRSA are twice likely to get recurrent infections. Previous studies have shown that these bacteria move from one person to another among people who live under the same roof, causing infections that reoccur and can be life-threatening in five to ten percent of cases.
According to a US study that is published in JAMA Internal Medicine, environmental contamination can produce a place for infection in the home, playing a big role in recurrent MRSA.
Researchers swabbed 11 items from the homes of 83 MRSA patients for over 6 months, including television remotes, furniture, doorknobs, toys, light switches, couches, computers, kitchen appliances handles, and toilet seats. Throat, nasal, and inguinal cultures were also collected from consenting members of their household.
These bacteria were found living in 24.4% of the home. The patients whose homes had contaminated items were very likely to contract MRSA again.
How You Should Wash And Disinfect Furniture And Other Surfaces To Stop The Spread Of MRSA Infection
- You can use cleaners or detergents. These products remove soil, dust, dirt, germs (bacteria, viruses, fungi), and organic matter. These products remove dirt and germs from surfaces so they can be rinsed off with water. Cleaning surfaces with a detergent is very important so that it will remove dirt that doesn’t allow disinfectants to work. Some disinfectants come with a cleaning agent, read the label of the product you are buying.
- Disinfectants are chemical products formulated to kill germs. Disinfectants that are effective at killing Staphylococcus aureus are also effective for getting rid of MRSA. On the label of the product, a list of the germs that it can kill and an Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) registration number should be found. Disinfectants are also sold at the grocery store and other retail stores and may be very useful when someone has an infected wound.
Which Disinfectants Can You Use Against MRSA?
When buying a disinfectant, check its label on the back of the container. Most disinfectant manufacturers will provide a list of germs their product can kill on the label. Disinfectants that fight against Staphylococcus aureus or staph will also fight MRSA.
What To Clean To Prevent MRSA From Spreading
When you are cleaning and disinfecting your home, pay more attention to surfaces that usually contact people’s skin, like chairs, lockers, desks, faucets, gym equipment, benches, remote controls, and light switches. Make sure you clean surfaces that come in contact with uncovered cuts, wounds, or boils. Also, cleaning the hands frequently and covering wounds properly prevents MRSA from spreading.
Large surfaces like walls and floors have not been associated with the spread of these bacteria. There is no evidence that cleaning or spraying such surfaces with disinfectant will prevent infections more effectively than spraying surfaces that are touched frequently or that have been exposed to cuts and wounds.
How Do You Prevent MRSA Infections?
Currently, there is no available vaccine to prevent MRSA. The best prevention is to wash your hands before drinking, eating, applying products on your hair and skin, touching your eyes, nose, face, and after using the toilet.
It is important to wash your hands very well with warm water and soap and use a paper towel to dry your hands. If you do not have access to soap and water at the moment, use a hand sanitizer. Make sure the sanitizer is alcohol-based. You can use sanitizers if your hands are not visibly dirty.
Certain bacteria can live on surfaces for months. Cleaning surfaces with disinfectants and household cleaner will help prevent the spread of these bacteria.
CA-MRSA can be spread when people use the same towel or sports clothing and equipment that would come in contact with the skin. People who play organized sports should use their clothing and pads.
Can I Contact MRSA?
This bacterial infection is very contagious under certain situations (when there is skin alterations or damages); it spreads through person-to-person contact, or indirect contact such as using an infected person’s towel or clothing, and even from gym benches. MRSA only needs a small break into the skin or mucosa to establish itself.
No break-in means no infection. This is why infected pregnant women seldom infect their fetus or infants, but activities like saliva exchange, kissing, and sexual contact (which is less likely to transfer the bacteria to another person) can cause an MRSA infection if the mucosa or skin is damaged.
If hospital patients have MRSA Pneumonia, they may infect others through the air by droplets that are contaminated. Bodies of dead MRSA patients often have viable MRSA, which can infect other people on their surface. The incubation period for this organism ranges from 1 to 10 days.
MRSA Contagious Period
As long as an individual who is infected or colonized with MRSA has viable MRSA bacteria on him, MRSA can be transmitted.
A person that is colonized with these bacteria (one who has MRSA present in his or her body) may be contagious for an unspecified period. Also, the organism can live on some surfaces for 2 to 6 months if the surfaces are left unwashed or unsterilized.
How To Know If You Have MRSA
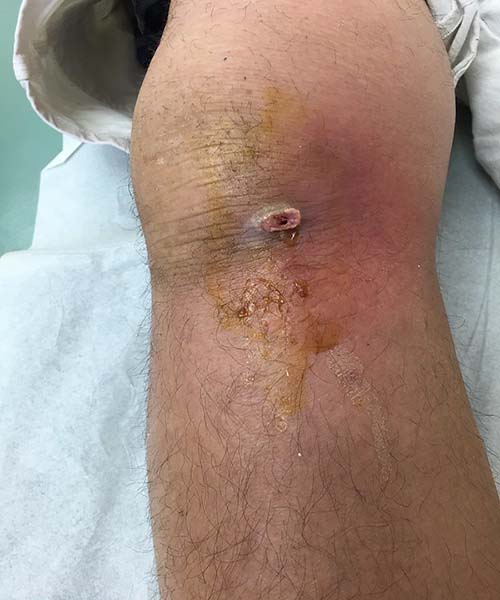
Most MRSA infections on the skin first show up as a reddish bump that becomes swollen and painful in a short time. It also becomes warm and contains or drains pus. This infection can appear almost anywhere on the body.
An infected person may also develop a fever. Patients that are hospitalized patients may show pneumonia, surgical wound infections, or sepsis. The best way to diagnose MRSA, however, is to have your physician culture the bacteria (biopsy, skin lesion, or nasal swab) and then show that they are resistant to some antibiotics.
How Is MRSA Transmitted?
In the community, MRSA is spread from one person to another by direct contact. It can also be spread by indirect contact since the bacteria can live on objects like benches, towels, shaving equipment, clothing, and other objects. MRSA needs a breach, such as a cut on the skin to infect a person.
MRSA that is spread in the hospital can be spread through above methods and also by blood, droplets in the air, and saliva. Hospital patients with MRSA are usually put under isolation conditions to help prevent the spread of MRSA.
MRSA carriers who are colonized with the bacteria are less likely to infect others; transmission is possible if the person is infected.
How Do You Treat MRSA Infection?
If you have MRSA on your skin or your nose, and you are healthy, you do not need any treatment, and you should go about your normal activities. Even though you do not pose a health risk to your family, your colleagues, or the public, make sure you wash your hands regularly with soap and water.
You can rub a hand sanitizer that has alcohol on your hand after touching surfaces. These will help prevent the spread of the organism.
Mild MRSA infections of the skin may only require warm compresses or draining if there is an abscess. F needed, your health care provider will prescribe antibiotics.
You May Like These Articles As Well:
What Causes Erectile Dysfunction: Everything You Need to Know