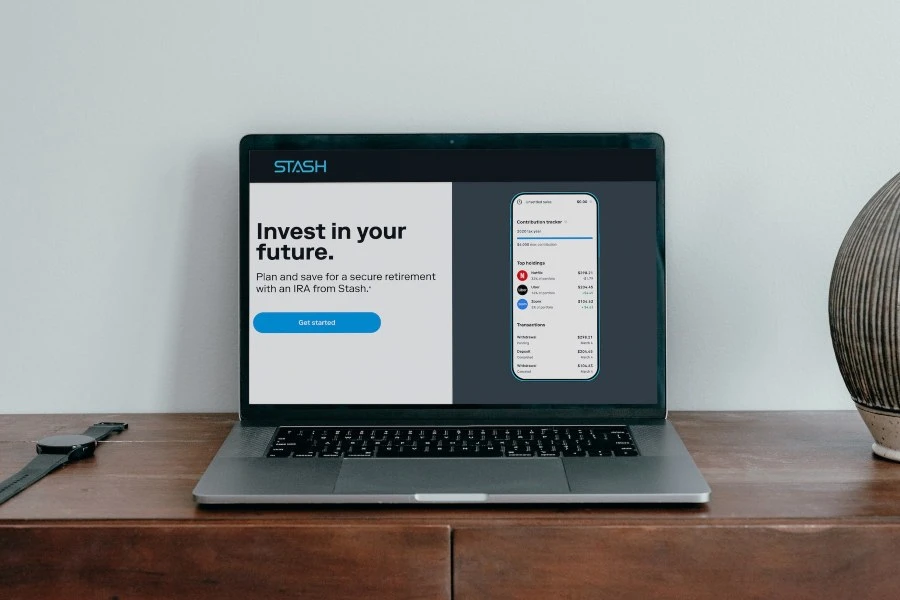
In digital marketing, landing pages are an important tool, regardless of your industry.
If you hire an SEO agency for lawyers or any other profession, they’ll likely help you set up landing pages, so what’s the goal of doing so, and what do these pages achieve?
We’ll detail what to know about landing pages below within the context of a larger digital marketing strategy.
1. The Basics Of Landing Pages
A landing page is not, contrary to popular belief, just any page that a visitor lands on when they click a promotional link or ad.
Campaigns use a lot of website resources as their landing pages, such as their “contact us” pages, but that doesn’t make them landing pages.
A landing page is actually a page that stands on its own, not linked to your website navigation. The entire goal of a landing page is to convince a visitor to take action. To go back to the example of a lawyer—a landing page might be something that your SEO team sets up to get a particular type of client to call you for a consultation.
Research indicates companies that use 40 or more landing pages generate 120% more leads than businesses using less than five.
Someone quite literally lands on your landing page after clicking an ad from Google or on social media, or maybe a link they get in an email.
The difference between a landing page and a web page is that a landing page has a single goal. That’s the call-to-action or CTA. Web pages can have a lot of goals. The focus of a landing page that’s singular is one of the primary reasons they increase conversion rates and reduce the cost of acquiring a lead or new client.
2. Homepage vs. Landing Page
We’ve touched on this a bit already, but when you compare a homepage and a landing page, you’ll see some key differences.
One is that a homepage is probably going to have a lot of links leading to other pages. A landing page will only have one link in most cases.
The homepage has dozens of possible distractions, but a landing page Is laser-focused, which helps increase conversions as well.
A landing page can serve the needs of visitors in a very different way than a homepage. The landing page has every feature to turn a visitor into a client or customer, while a homepage can provide information, let the visitor go anywhere else on the site, and explore products or services.
3. Are There Different Types Of Landing Pages?
There are two broad types of the landing page, and they’re classified by the goals of each one.
The first is a lead generation landing page or a lead capture page. There is a form that’s used for lead data collection, like email addresses of visitors.
A landing page can be used for list building, and sometimes these landing pages will give away something free in exchange for contact information, like an eBook.
The second category of a landing page is a clickthrough page. These are used more by SaaS and eCommerce marketers because these go straight to sales or subscription options. These pages will have a button that will send a visitor right into a checkout process, or it may complete a transaction.
4. Driving Traffic To Landing Pages
When you have a sales funnel, you need people to visit your landing page for it to be effective.
There are a few sources of traffic you can rely on.
One is paid search traffic. When someone enters a query, then they’ll see ads in their search results. Pay-per-click ads are created and paid for by marketers. You can target these ads based on search terms, demographics, or interests.
You create an ad and then get to choose where your visitor is taken when they click it.
Another way to drive traffic to a landing page is with paid social traffic.
Email campaigns can be an effective marketing channel, and when you combine emails and landing pages, you can nurture your current relationships with your clients and build new ones.
Finally, you can also drive traffic to a landing page organically. Organic traffic is a reference to any visitor coming from an unpaid source, like Google.
5. Features Of A Strong Landing Page
If you want a landing page that converts, remember the following features:
- Try to target long-tail keywords. These are specific and have four or more words usually. It’s generally easier to rank for long-tail keywords than short-tail keywords because they’re less competitive. Since landing pages will have a very specific call-to-action, then they work well with naturally placed long-tail keywords.
- Segment traffic. Your targeted audience probably includes more than one persona, so you want to make sure that you’re using the right approach to target each. A separate landing page for every segment of your targeted audience is more work upfront but is also more likely to engage visitors to your landing page.
- Improve loading speed. You aren’t going to rank well, nor are you going to hold visitors’ attention if your landing page loads too slowly. Users are impatient, and the slower your page, the less likely your chances of converting.
- Get backlinks. Backlinks point from other sites to your landing page, and they send traffic to you. Plus, when you have a lot of backlinks, it’s a vote of confidence to a search engine.
- Create a great headline. You want a compelling headline that’s going to get attention. You need your visitors to stay on your page for long enough for a conversion to happen.
- Try to put your CTA above the fold. The CTA needs to be one of the initial elements that a visitor sees, although it’s not always possible. If you aren’t putting it above the fold, use directional cues to show visitors where your CTA is.
Finally, include social proof if you have it. For example, in your copy, you might include testimonials and reviews from your happy clients or customers.
Social proof is a good way to convert visitors who could have otherwise been on the fence.








